Table of contents
No headings in the article.
#day12 of #90daysofdevopschallenge
cd - Change directory
Use this command to navigate to different directories in the file system.
Ex.
cd pictureswill take you to the "pictures" directory.cd ..- Move one level up.cd- To change to a particular directorycd /- Move to the root directoryman - Access manual pages. This command provides documentation for other commands. For example,
man lsdisplays the manual page for the "ls" commandls - List files and directories. This command shows the contents of the current directory. Adding options like -l or -a (for hidden files)provides more detailed information.
ls -R- lists files in sub-directories as wellls -a- lists hidden files as wellls -al - lists files and directories with detailed information like permissions, size, owner, etc.
pwd - Present Working Directory.
It displays the path of the current directory you are in.
mkdir - make directory. Use this command to create a new directory. For example,
$mkdir git_datawill create a directory named git_data in the current location.rm - Remove files or directories. This command deletes files and directories
permanently. To remove a file, use rm filename. To remove a directory and its contents, use the rm -r directory name.
cp - Copy files and directories. Use this command to make copies of files or directories. For example,
cp myfile.txt /path/to/destinationwill copy "myfile.txt " to the specified destination.mv - Move or rename files and directories. This command is used to move files or directories to a different location or rename them. For example,
mv file.txt /path/to/destinationwill move "file.txt " to the specified destination.cat - Concatenate and display file content. This command shows the contents of a file on the terminal. For example, cat file.txt will display the content of "file.txt"
grep - Search for text within files. Use this command to search for specific text within files. For example-
grep keyword file.txtwill search for the keyword in "file.txt".chmod - Change file permissions. This command is used to change the permissions of a file or directory. For example, chmod +x script.sh makes "script.sh " executable.
sudo - Execute a command with superuser privileges. Use this command to run a command as the super user(administrator).it is often used for system administration tasks. For example,
sudo apt-get updateupdates the package lists with administrator privileges.apt-get - Package manager command. This command is used to install, update or remove software packages in Debian-based distributions. For example, sudo apt-get install package-name installs a package.
gzip- Compress or decompress files using gzip.
gunzip-Decompress files compressed with gzip.
find - Find files and directories matching a pattern.
wget - download files from the web. Use this command to download files from the internet. For example,
wget https://example.com/file.txtwill download "file.txt" from the specified URL.ping - Check network connectivity. This command is used to check if a network host is reachable. For example, ping google.com.
adduser UserName - Adds a new user to the system.
passwd -l UserName - Changes the password of a user.
userdel -r UserName - Removes a user from the system, including their home directory.
usermod -a -G GroupName UserName- Adds a user to a specific group.
deluser UserName GroupName - Removes a user from a specific group.
touch - Create an empty file.
awk - pattern scanning and processing language.
sed - stream editor for filtering and transforming text.
head - Display the first few lines of a file.
tail - display the last few lines of a file.
wc - Count lines, words, and characters in a file.
sort - Sort lines of a file.
diff - Compare two files line by line.
chown - Change the owner of a file or directory.
chgrp - Change the group ownership of a file or directory.
ps - List running processes.
top - Display system resource usage and process information.
kill - Send a signal to a process to terminate it.
du - Display disk usage of files and directories.
df - Display free disk space on the file system.
mount - Mount a file system.
umount - Umount a file system.
ssh - Secure shell remote login and command execution.
scp - Secure copy files between hosts.
rsync - Remote file and directory synchronization.
curl - Transfer data from or to a server using various protocols.
ftp - File Transfer Protocol client
sftp -Secure File Transfer Protocol client
telnet - Telnet client
nslookup - DNS lookup utility.
dig - Domain Information Groper. It is used for retrieving information about DNS name servers
netstat - Display network connections and statistics
ifconfig - Configure network interfaces
route - Display or modify the routing table
iptables - Firewall and packet filtering utility
hostname - Display or set the hostname of the system
date - Display or set the system date and time
uname - Display system information
whoami - Display the current user ID
id - Display user and group information
su - Switch user to become another user
groupadd - Create a new group
groupmod - Modify a group
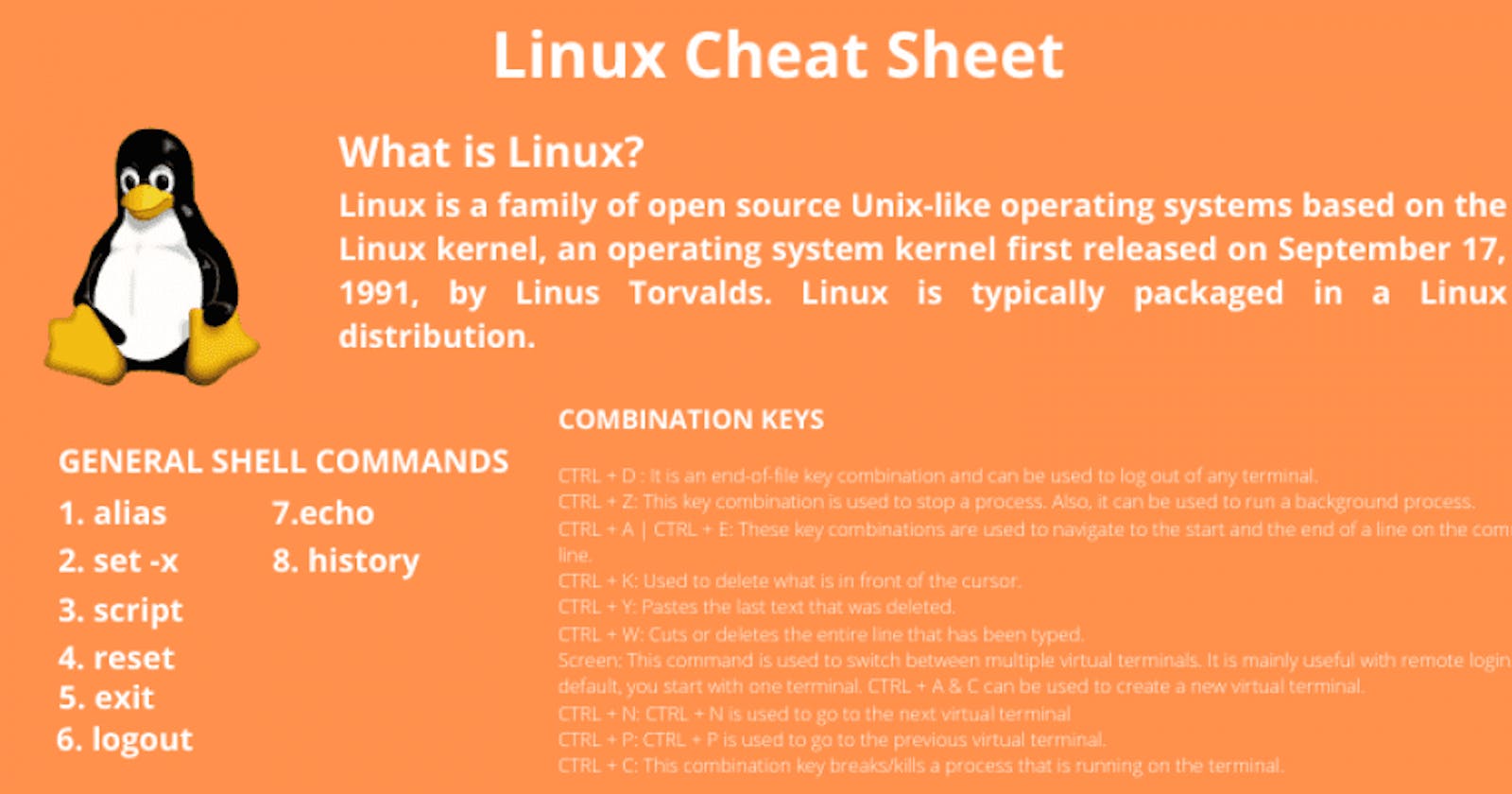
history - Display command history
echo - print a message to the terminal
hwinfo - Displays detailed hardware information
free - Displays memory usage
vmstat - Displays system memory, processor, and I/O statistics
iostat - Displays CPU and disk I/O statistics
uptime - Displays system uptime and load averages.
crontab - Schedules recurring tasks
traceroute - Traces the network path to a remote host
less - Display file contents in a paginated format
more - Display file contents one page at a time
chroot - Change the root directory for a process
alias - Instructs the shell to replace one string with another string while executing the commands
reset - The best method to reset your terminal is with the reset command
exit - Used to exit the shell where it is currently running
logout - Performs the task of logging out the logged-in user from the system
script - Used to make typescript or record all the terminal activities
Thanks for reading!!!!!